The tight integration between design and simulation tools ensures a fast, streamlined workflow and helps eliminate errors in the early stages of the process.
QForm Direct is a computer-aided system for automated design of bulk forging preforming dies.
QForm Direct makes it possible to create a 3D model of the preforming dies for bulk forging processes and import the geometry into QForm to verify the result. The principle of QForm Direct is simple, but the calculation methods are based on thorough scientific research and analysis. You just need to use the finish forging dies as initial data and after the automatic generation to pick the best surface for preliminary dies. Designed 3D models can easily be imported into the QForm to check the process.
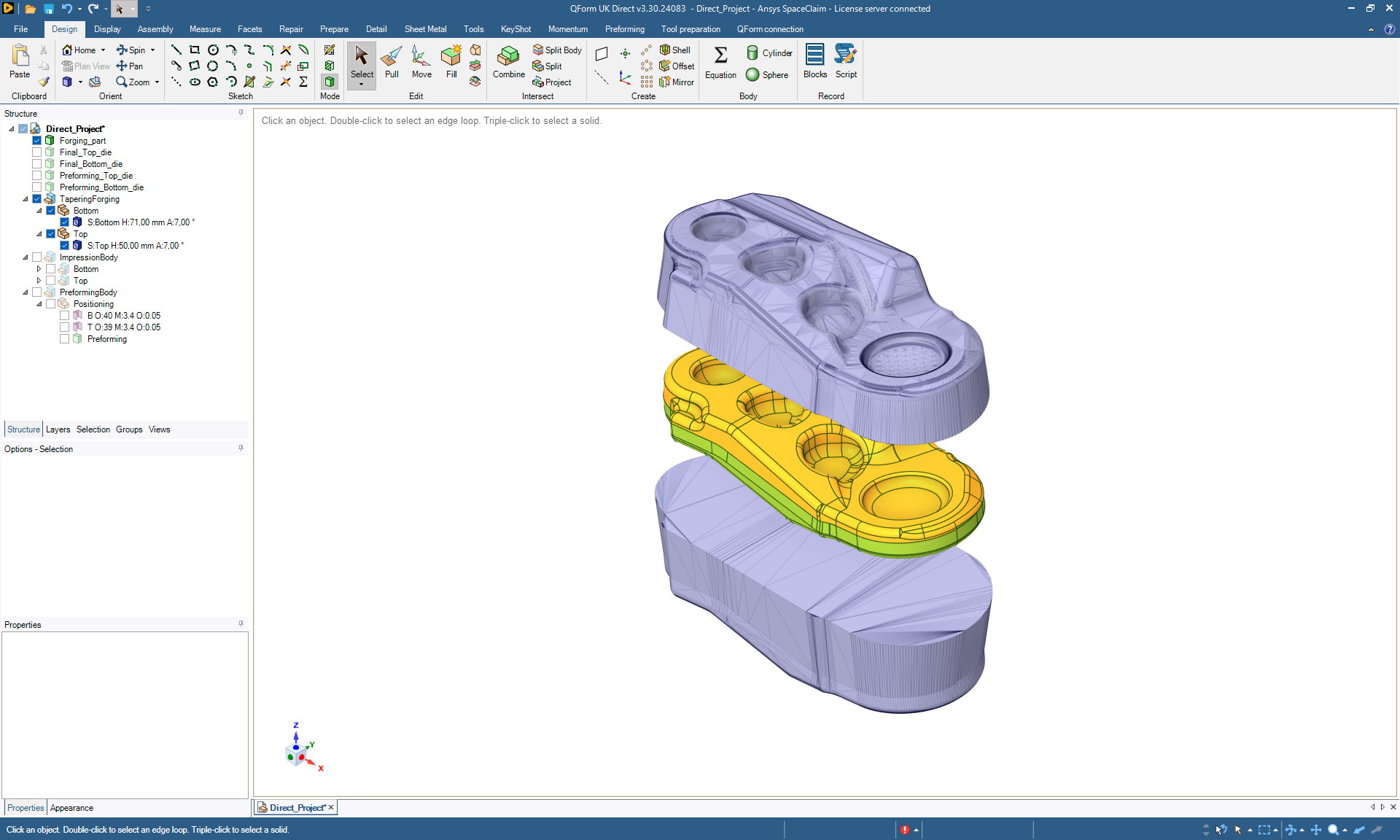
QForm Direct contains full functionality of a CAD software and uses QForm calculation algorithms to generate surfaces. It is possible to refine die geometry in QForm Direct: add fillets, holes, and other necessary technological elements. The created geometry can be used for both QForm simulation and CAM systems.
Discover how easy it is to create a 3D model of preforming dies for bulk forging processes using QForm Direct. These tutorials provide a step-by-step guide to the design process, from forging body creation to the final preparation of preforming dies. While the process is intuitive and simple, it is powered by impressively complex computational algorithms.
To construct a preform cavity, QForm Direct uses the method of isothermal surfaces, which is similar in its approach to the method of constructing equipotential surfaces of an electrostatic field. The principle of the method is based on building a volumetric thermal model. The thermal model is formed by two surfaces: the surface of the final die engraving and another surface, constructed according to specific rules, which serves as a heat source. Using the finite element method, QForm’s calculation algorithms determine the steady-state thermal field within the volume and generate isothermal surfaces. To create the shape of the preform cavity, it is only necessary to select an intermediate isothermal surface, which will be used as the model of the die engraving. Once the thermal field has been calculated, generating each new surface takes only a few minutes.
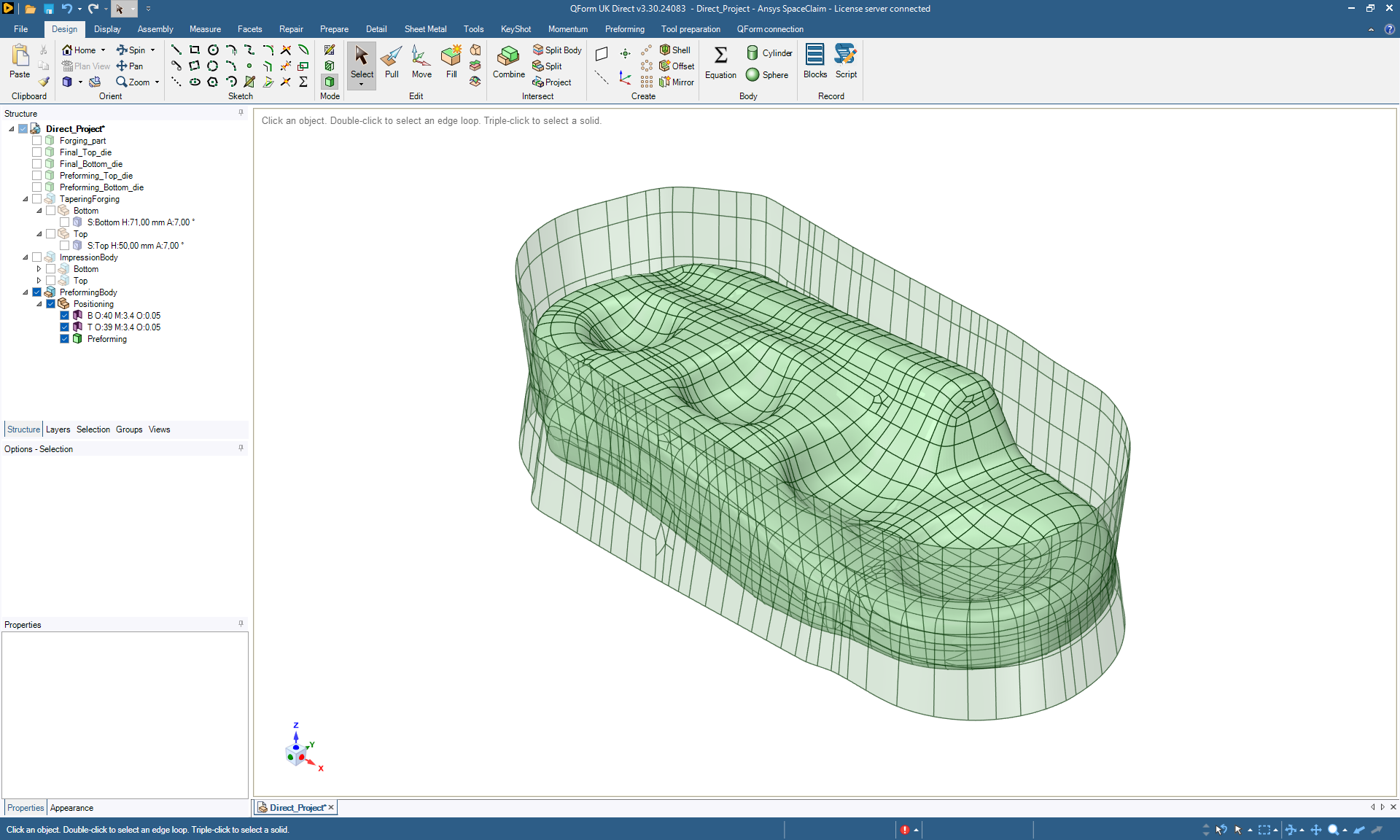
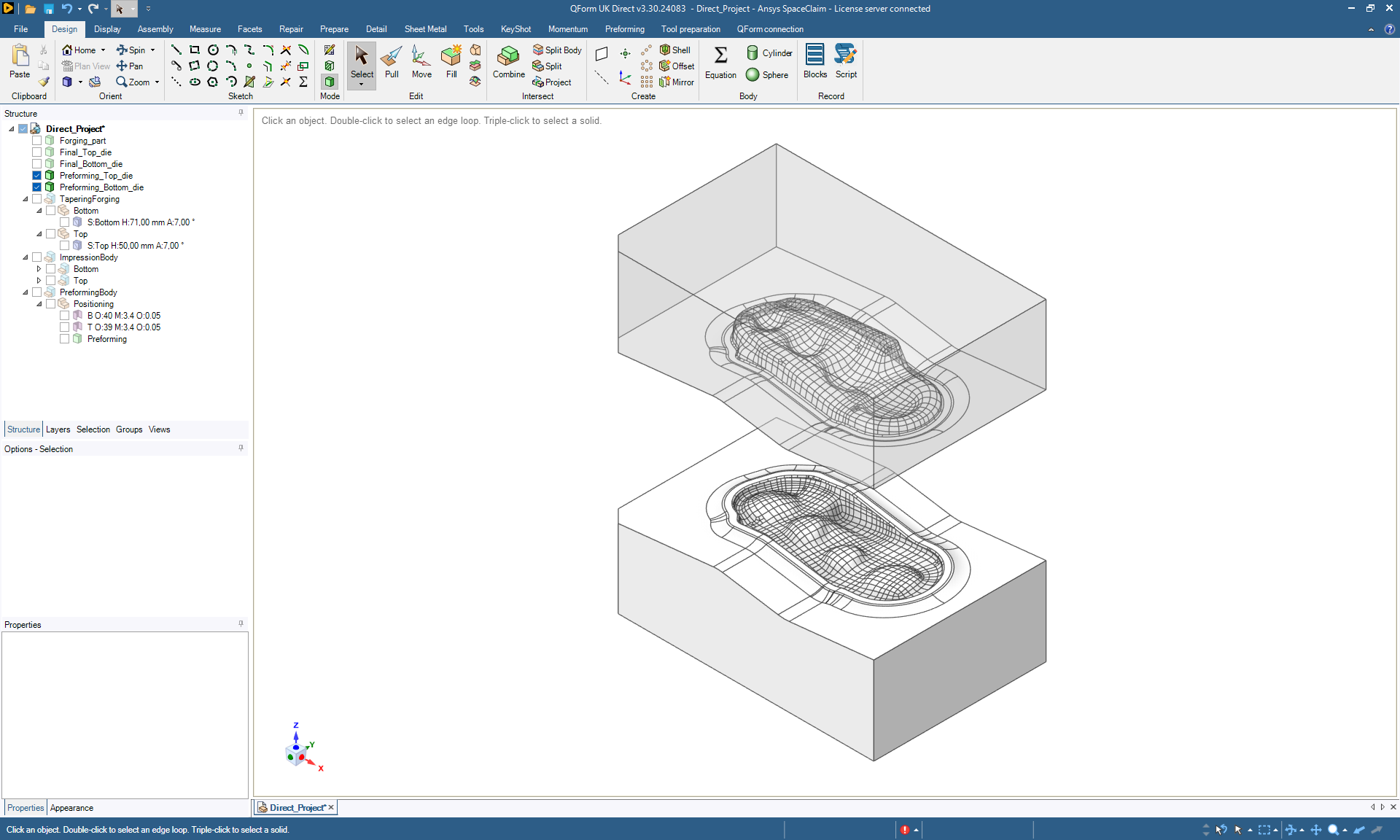
QForm Direct contains full functionality of a CAD software and uses QForm calculation algorithms to generate surfaces. It is possible to refine die geometry in QForm Direct: add fillets, holes, and other necessary technological elements. The created geometry can be used for both QForm simulation and CAM systems.
QForm is an indispensable tool for the development of closed-die forging technological processes. The program allows simulation of metal flow in different dies on any kind of equipment to predict possible defects (non-filling of a die impression, laps, flow-through defect, etc.)
The program shows temperature fields, the stress-strain state indicator in the forging and the tools, as well as the fibrous microstructure and other parameters necessary for development of forging technology. The analysis of forging load and the energy consumed allows the selection of the optimal equipment. QForm allows an engineer to optimize the process, avoiding defects, decreasing metal consumption and increasing productivity.
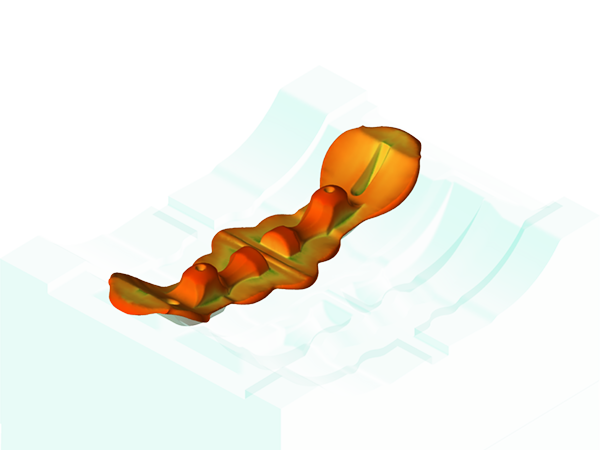
The video showcases forging of a connecting rod on a mechanical press, featuring a unique preforming step using reducer rolling with four actions. This is followed by flattening, blocker forging, and finish forging. The reducer rolling preform promotes a favorable fibrous microstructure, demonstrated in the final stage.
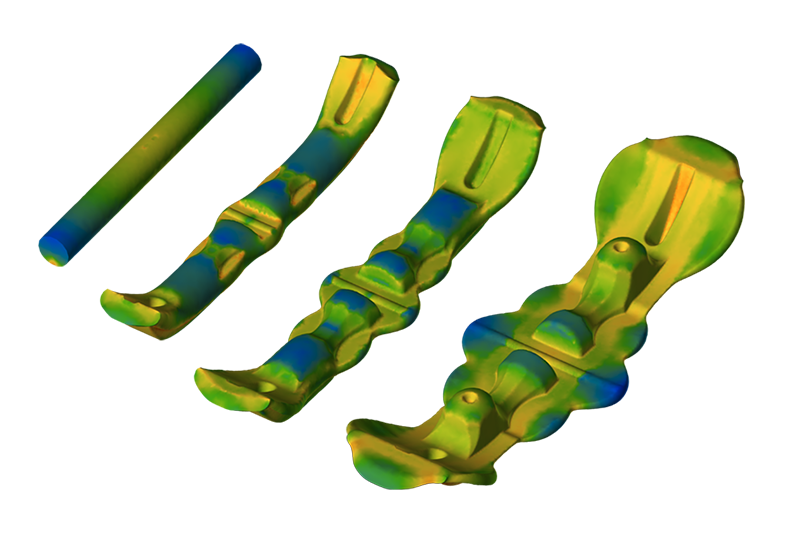

QForm simulation enables efficient process development without costly shop floor tests. It helps designers optimize workpiece and tool parameters, reducing material waste, extending tool life, improving forged part microstructure, and ensuring ideal temperature control throughout heating, forging, and heat treatment.
The forging technology can be optimized to reduce the number of forging blows and increase die life by minimizing load and deformation work. The simulation allows the user to develop the optimal design of the forging, reduce wasted material in the forging and optimize the preforming operations.